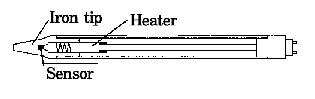
TECHNOLOGY RESPONSE
Home > Data Room > Technology response
lead-free solderingResponse to quality improvement`  Importance of Temperature Selection in Lead-free Soldering Importance of Temperature Selection in Lead-free Soldering
Soldering bonding is a method of bonding by chemical reaction between the base material to be bonded and the bonding alloy, and the melting point of the alloy and the heat source (temperature) of the base material are important requirements during bonding.
Additionally, the role of Flux, the main agent of the chemical reaction with the base material during soldering bonding, is that the component is rapidly oxidized at high temperatures, which loses the characteristics of the base material cleaning and bonding chemical reaction required for bonding, and appears to be a lack of surface tension and a lack of spreadability of bonding alloys. Therefore, maintaining a constant temperature and setting an appropriate temperature in soldering are the most important conditions among the components of soldering bonding quality. It is important to maintain the optimum temperature  Optimal low-temperature soldering (pb free) Optimal low-temperature soldering (pb free)1. Select the lowest optimum temperature possible to preserve the Flux characteristics. - If the soldering temperature is high, the Flux component in the lead is oxidized, resulting in defects such as a decrease in spreadability of lead, a decrease in bonding tensile strength, a Flux foreign matter, and a defect in appearance. - At higher temperatures than necessary, the lifespan of the pharyngeal tip is rapidly shortened, causing defects. 2. Please check the necessary heat source of the base material and the melting point conditions of the bonding alloy to be used. - The required heat source of the base material to be bonded during soldering must be secured at least 250°C (pb free). - If necessary, please consider using the preheater of the base material. - Please check the melting point of the bonding alloy because the melting point of the bonding alloy varies depending on the components contained. 3. Please choose the best iron tip for heat transfer - The selection of pharyngeal tips in securing and spreading heat sources is a very important requirement. - Please select a tip with a specification that is 0.5 to 1mm larger than the workland. - Please refer to the Iron Tip application and select the appropriate iron tip specification. - Please check the angle of the contact surface so that heat transfer can be optimized. 4. Please check the Flux characteristics of the usage payment. -There are various contents ranging from 1.5 to 8% for each company, and there is also a manufacturing know-how for each company, so please thoroughly review it, respond to high temperatures, and select an appropriate product with little residue.
5. Please check the temperature at least once before the business starts on the 1st. - If the display temperature and the actual temperature are more than 5℃, please take immediate action and use them.
- Temperature maintenance is the most important soldering condition, and when the temperature changes, it becomes difficult to preserve the characteristics of the flux and the heat source of the bonding alloy and the base material changes In this case, it will have a significant impact on the quality of soldering. - Therefore, even if the bonding temperature is high or low, it will greatly affect the bonding quality. 6. Set the appropriate parameters for each task point. - Conditions such as temperature and 1st and 2nd soldering time, amount of lead used and supply speed, cylinder time and speed, etc. will be checked for each type of work after checking the continuous quality
It is recommended to standardize it, and in the event of a defect, please clearly analyze which part of the 4M is the problem and respond to it, change the conditions from time to time Ordering is an obstacle to fundamental defect analysis measures. 7. Please consider using N2 Gas for points that use small amount of lead and slide soldering such as LCD&FPC. - If a small amount of lead is used, there may be problems with solder quality due to a lack of flux.
- In the case of continuous soldering, such as slides, continuous soldering is performed with the initial supplied lead and flux components oxidized, so use N2 Gas, Oxidation needs to be delayed, and the effect of preheater using N2 Nozzles can be expected as a countermea-sure for excessive heat absorption of the base material. * The optimum temperature also prevents scattering of lead balls and flux, and also extends the life of the pharynx. * When setting the temperature, set it as high as +20~30℃ from the minimum temperature. This is to anticipate and set incomplete factors such as changes in the base metal, changes in the iron tip, changes in working conditions, and setting the working conditions of the user. - For example In the case of a single pattern with a diameter of 2mm or less, the actual heat source required is about 290°C to 300°C, but it is set to 330°C.  Typical soldering temperature (based on pb free) **Depending on the heat source of the base metal. Typical soldering temperature (based on pb free) **Depending on the heat source of the base metal.ㆍWhen working with Apollo Robotics TM&TS
Some of this material is referred to the Ishikawa metal data.
 Precautions for selecting unpaid payment Precautions for selecting unpaid payment
* If there is no special problem with the work, please use Sn96.5%, Ag3.%, and Cu0.5% of lead-free.
Reliability (strength, spreadability, etc.) is verified and is the most commonly used lead-free. * Due to the nature of the product, lead-free Sn is required if high temperature response is required, and Bi or In is required if low temperature response is required due to problems such as thermal shock Please consider using the included lead-free payment. * The manufacturing technology of Flux varies greatly depending on the lead manufacturer, so please pay attention to the following. Flux technology is the most important variable in maintaining the quality and productivity of lead-free soldering. 1) Flux-containing scent: Good content of 3-4%, in some cases, for high-temperature soldering and high-speed soldering, please consider 6% lead-free. 2) High Temperature Response: Please receive information on the optimal temperature of the flux used by the manufacturer and compare and select conditions such as spreadability, surface cleaning capacity, lead ball, flux residue, surface tension, etc. 3) Residue Response: In general, it is recommended to use Rosin Flux, but if there is an external problem such as a Flux residue, please use Resin Flux. For residue problems, the main reason is to leave high temperature after solder injection, so proper cleaning cycle and high speed soldering are effective for Flux residue response. For robot soldering, Flux residue response is possible with techniques.  Comparison of advantages and disadvantages by component Comparison of advantages and disadvantages by component
 Free solder alloy characteristics Free solder alloy characteristics1. Appearance condition While Sn-Pb soldering has a glossy surface, pb-free soldering has a rough surface. Among them, pb-free soldering with Ag has a strong tendency. In addition, pb-free soldering with Bi makes the entire surface look dull.
2.creep characteristics According to the creep test results, pb free soldering has superior creep characteristics compared to Sn-Pb soldering.
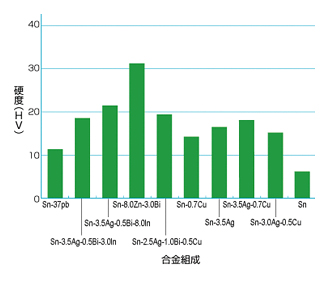
3. Sir Vickers
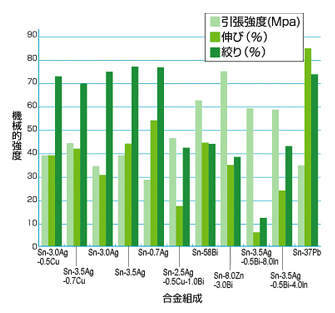
4. mechanical strength
|